Archeologists Uncover 200 New Stones, 15 Temples At Göbekli Tepe
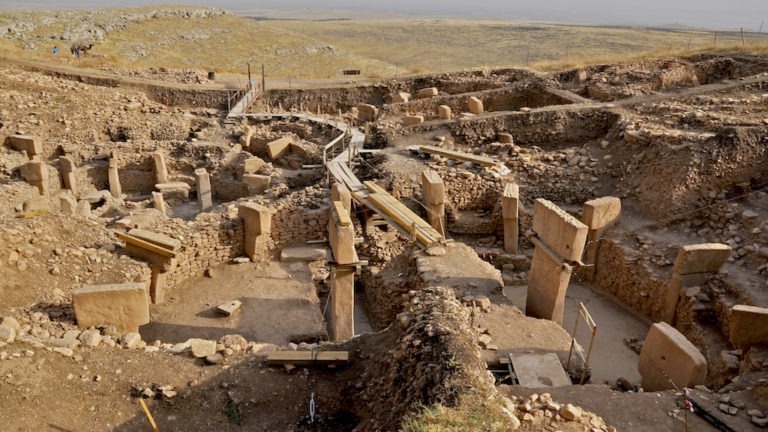

Archeologists recently discovered at least 15 new megalithic temples and over 200 standing stones at Göbekli Tepe in southeastern Turkey, the oldest archeological site in the world. The excavations predate what was originally thought to be the oldest evidence of human settlement, Çatal Höyük, and are so extensive they will likely require another 150 years of excavation.
The site was reopened partially in February, after being closed to visitors so archeologists could work on its restoration. UNESCO recently added Göbekli Tepe to its list of world heritage sites, with the majority of the complex remaining underground.
Göbeklie Tepe, meaning “potbelly hill,” has baffled archeologists for years, after it was dated to have been built before modern agriculture or the discovery of metal, despite the multitude of carved obelisks used in its construction. These massive stones are T-shaped, weighing between 40 to 60 tons, and standing between 10 to 20 feet tall.
According to mainstream archeology, the site served no practical purpose because it appears that it was not used for housing, and was allegedly built by hunter-gatherers. It was discovered by archeologist Klaus Schmidt, who excavated the site from 1996, until his sudden death in 2014.
But Göbekli Tepe is comprised of intricately carved stones as large as the rocks at Stonehenge, built 7,000 years later. The idea that a group of hunter-gatherers with primitive stone tools could construct a site of this magnitude is astonishing. Alternative theorists believe there may be more to the story.
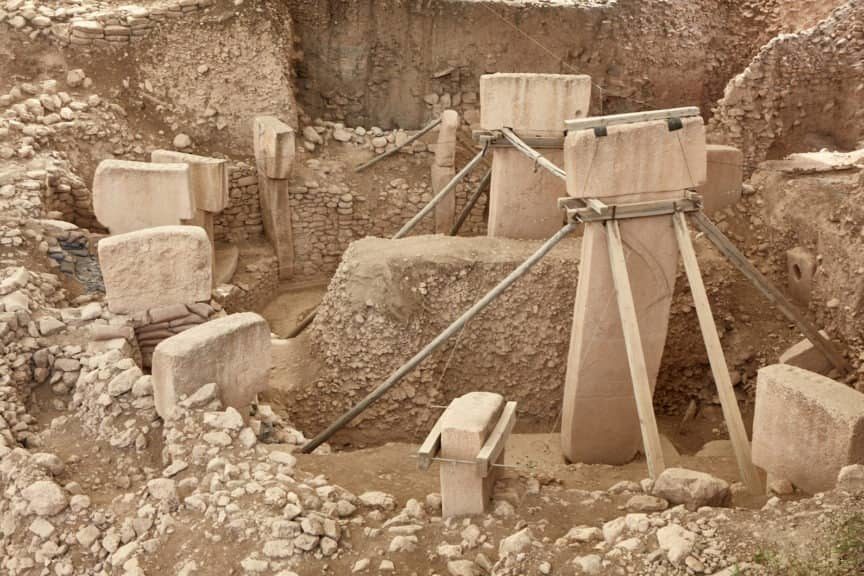

Others believe the site could be evidence of a lost civilization that drastically predates mainstream archeology’s official timelines. Graham Hancock points out that the site contains the first perfectly north/south associated buildings, alignments to specific star groups and specific moments of the year, meaning this culture had a strong grasp on astronomy.
Boston University Professor Doctor Robert Schoch, posited the idea that an ancient, advanced culture predating traditional civilizations may have existed before the end of the last ice age, before it was wiped out in a cataclysmic event around 9,700 BCE.
Schoch says he believes that a solar induced dark age occurred after a massive solar flare took place, forcing existing civilizations to retreat underground, or as is the case with Göbekli Tepe, to bury their structures for preservation. He believes this culture eventually died out, as human populations descended back into a stone age, until the cycle of civilization sprung up again in Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt.
Schoch points to the Sphinx and the water erosion hypothesis as potentially having a connection to this culture. Schoch and other proponents of alternative archeological timelines believe the Sphinx predates ancient Egyptian civilization, due to water erosion on the side of the sphinx; the annual average rainfall that would have been enough to cause this type of erosion ended thousands of years before the Sphinx was allegedly built.
As Graham Hancock likes to say, “stuff just keeps on getting older.”
Learn more about Göbekli Tepe from the research of Andrew Collins in this episode of Beyond Belief:
Were the Gods of the Sumerian Kings List Real?

Our history books are continually being tested and challenged, but few discoveries have thrown a wrench into the officially accepted narrative of man’s origin like the DNA of Alfred Perry. Thanks to a chance submission of this one man’s blood to a genealogy laboratory, scientific theories of our species’ origin have been turned upside-down.
The story began in 2013, when a female relative of Alfred Perry, a South Carolina man, submitted a sample of his DNA to trace the family’s genetic roots. It turned out Perry’s DNA was not only rare, but it reset the entire timeline for human existence on this planet. Perry’s Y chromosome contained a signature unlike any other.
Y chromosomes represent the genetic factor that determines the male gender, and from Perry’s DNA, scientists were forced to admit that the common ancestor for his lineage was roaming the earth some 340,000 years ago. Previous to Perry’s DNA sample, scientists believed the origins of humankind traced to an original “Adam” somewhere around 140,000 years ago.
Perry’s DNA may support the theory that this planet has been home to earlier human civilizations that somehow became extinct—or nearly extinct—and that humanity may have been involved in a reboot, so to speak. This theory is supported by an ancient artifact known as The Sumerian Kings List—a written history of kingship in ancient Mesopotamia discovered in Sumerian cuneiforms.