Scientists Now Say Interstellar Object May Have Been Alien Probe
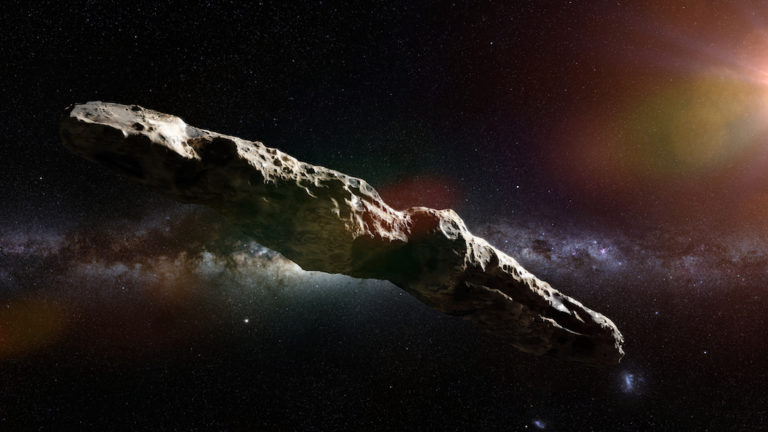

Harvard scientists reexamined the bizarre, interstellar space object known as “Oumuamua,” which rocketed through our solar system late last year, resurrecting the possibility that it may be an alien probe. Academics and scientists were quick to write off the cigar-shaped object as a previously unknown type of bolide – a comet or asteroid – propelled in a highly unusual manner, but their observations are once again, being challenged.
Oumuamua, which means “a messenger sent to reach out in advance,” was first observed by Robert Weryk at the Pan-STARRS 1 telescope in Hawaii. He measured the object to be several hundred meters in length, or the size of a large sports stadium.
The size and shape of the object were calculated to be able to hold up to collisions with space dust and debris while maintaining enough momentum to travel the vast distance between stars, but recent examinations found a discrepancy in its mass-to-area ratio that doesn’t quite add up.
“Known solar system objects, like asteroids and comets, have mass-to-area ratios orders of magnitude larger than our estimate for ‘Oumuamua,” said Shmuel Bialy and Abraham Loeb of the Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics.
“If radiation pressure is the accelerating force, then ‘Oumuamua represents a new class of thin, interstellar material, either produced naturally, or of an artificial origin.”
They went on to speculate about the possibility of Oumuamua as a type of artificial satellite known as a lightsail, which is currently in development by the Breakthrough Initiative program founded by Yuri Milner and Stephen Hawking. Loeb is a member of the Breakthrough Starshot Initiative.
“The lightsail technology might be abundantly used for transportation of cargos between planets or between stars. In the former case, dynamical ejection from a planetary system could result in space debris of equipment that is not operational anymore and is floating at the characteristic speed of stars relative to each other in the Solar neighborhood. This would account for the various anomalies of ‘Oumuamua, such as the unusual geometry inferred from its lightcurve,” Bialy and Loeb said.
Oumuamua hurdled through our solar system at 58,000 mph when it was discovered on Oct. 19, 2017. The object was then propelled by the Sun’s gravity, causing it to blast off on a hyperbolic trajectory out of our solar system at a rate of 196,000 mph.
This exit speed was initially attributed to a combination of a gravity assist from the Sun and outgassing – the release of gasses from a comet as its surface heats. But scientists noticed that Oumuamua didn’t show the typical “coma,” or cloud of gas, one might expect from an outgassing comet, making its high escape velocity especially strange.
This led Loeb and Bialy to consider another potential for Oumuamua… a more exciting one.
“Alternatively, a more exotic scenario is that ‘Oumuamua may be a fully operational probe sent intentionally to Earth vicinity by an alien civilization,” the authors said.
Unfortunately it’s way too late for us to send a probe to Oumuamua or even to photograph it so that it could be studied properly, due to simply to its sheer speed and the distance it’s already travelled from Earth. Instead, Bialy and Loeb suggest we keep our eyes out for similar objects careening through our local celestial neighborhood.
For more on the potential techno-signatures of extraterrestrial civilizations watch this episode of Deep Space :
Is This a Solution to the Fermi Paradox?

A new theory has been devised on why aliens have never visited Earth, that we know of, as a possible resolution to the Fermi paradox.
Many who are curious about the existence of ETs have heard about the “Fermi paradox,” named after famous astrophysicist Enrico Fermi.
The story goes that in a lunchtime conversation with other astrophysicists who reasoned that, given the vast size and age of the universe it stands to reason, there must be other intelligent life out there, to which Fermi asked, “where is everybody?”
For decades people have tried to answer that question if there are so many possible ET civilizations, where are they? Now, astrobiologists Michael Wong, of the Carnegie Institution for Science, and Stuart Bartlett, of the California Institute of Technology offer their hypothesis, and it’s a bit dark.
Using studies of the growth of cities on Earth, they argue that civilizations grow infinitely but in a finite time. This infinite growth of population and overuse of energy will eventually lead to the death of the civilization or possibly saving themselves.
“We propose a new resolution to the Fermi paradox: civilizations either collapse from burnout or redirect themselves to prioritizing homeostasis, a state where cosmic expansion is no longer a goal, making them difficult to detect remotely.”