Scientists Are Now Using Sound Waves to Regrow Bone Tissue
The future of regenerative medicine could be found within sound healing by regrowing bone cells with sound waves.
The use of sound as a healing modality has an ancient tradition all over the world. The ancient Greeks used sound to cure mental disorders; Australian Aborigines reportedly use the didgeridoo to heal; and Tibetan or Himalayan singing bowls were, and still are, used for spiritual healing ceremonies.
Recently, a study showed an hour-long sound bowl meditation reduced anger, fatigue, anxiety, and depression, which is great news for mental health. But now, a new study out of the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology in Australia, showed physical healing using sound waves.
Scientists used high-frequency soundwaves to turn stem cells into bone cells in a medical discipline called ’tissue engineering,’ where the goal is to rebuild tissue and bone by helping the body to heal itself.
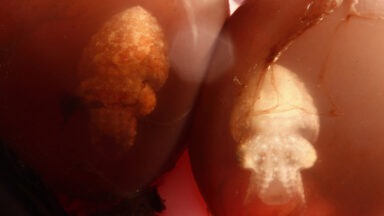
The researchers shot sound waves at tissue cells for 10 minutes a day over the course of five days. This magnified image shows stem cells turning into bone cells after being treated with high-frequency sound waves.
Co-lead researcher Leslie Yeo explained, “[W]e can use the sound waves to apply just the right amount of pressure in the right places to the stem cells, to trigger the change process.”
Professor Yeo and his team have spent over a decade studying sound wave effects on different materials, and have learned to use sound waves above 10 megahertz for the best results. In the past, the researchers point out, experiments to turn stem cells into bone cells were cost-prohibitive to scale up, and as cells had to be harvested from patients’ bone marrow, it could be extremely painful. But in this experiment, they used multiple types of cells, even fat cells that are much easier to extract from a patient.
They further argue that since the sound waves created in this experiment were generated by a low-cost microchip, their process will be quicker, easier, and less expensive than other methods. The next major challenge ahead: scaling the process so it can be put into medical use.
Artificial Intelligence Finds Missing Ghost Ancestor of Humans

Our ancestry as a species is intricate and convoluted. We know that Denisovans, Neanderthals, and the other iterations of our hominin ancestors interbred and evolved over hundreds of thousands of years. But while anthropologists have done their best to map out this complicated lineage, we’ve now reached a point in our evolution that machines can map our genealogy better than we can. Such was the case when a machine learning algorithm applied to our DNA roadmap found a new ancestor we didn’t even know existed.
According to a study published in Nature Communications, scientists fed DNA data from fossilized bones and modern humans into an A.I. algorithm that computed thousands of timelines to map out the possible evolutionary pathways based on what we know – or what we think we know – about our ancestors migrations, diasporas, and interbreeding to tell us if we were missing anything.
It turns out we were…
The new study found that a missing, archaic “ghost” ancestor played a significant role in the development of the human species, helping to propel us from primitive hominins to the highly intelligent beings we are today.
This ancestor was likely a hybrid of Neanderthals and the Denisovans – the hominin ancestor discovered in 2010, that five percent of modern humans can still directly trace their genealogy through.
And though the study’s authors are referring to this hominin hybrid as a “ghost” population, they also believe there might be fossil evidence of it found in the bones of a 90,000-year-old specimen of a teenage girl discovered in Siberia’s Denisova cave – the location where the original Denisovan fossils were found.
The discovery of the Denisovans has presented itself as one of the most profound and baffling finds for archeologists within the past decade as their fossil remains showed they existed for millennia alongside our other ancestors. Not to mention they appear to have been massive in comparison to other hominin species.
And by massive, they mean that a Denisovan wisdom tooth found in the cave was originally mistaken for that of a bear’s. And though wisdom teeth can vary in size, the anthropologist studying the specimen, Bence Viola, told National Geographic, “large teeth with massive roots would probably require massive jaws.”
Who were these gigantic Denisovans whom we know so little about, and even more baffling, what did their hybrid progeny with Neanderthal’s look like? These paradigm-shifting discoveries only add to the fact that we still have so much more to learn about our species’ history.
For more on the strange discovery of the gigantic Denisovans check out this episode of Ancient Civilizations :