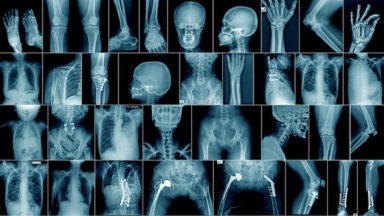
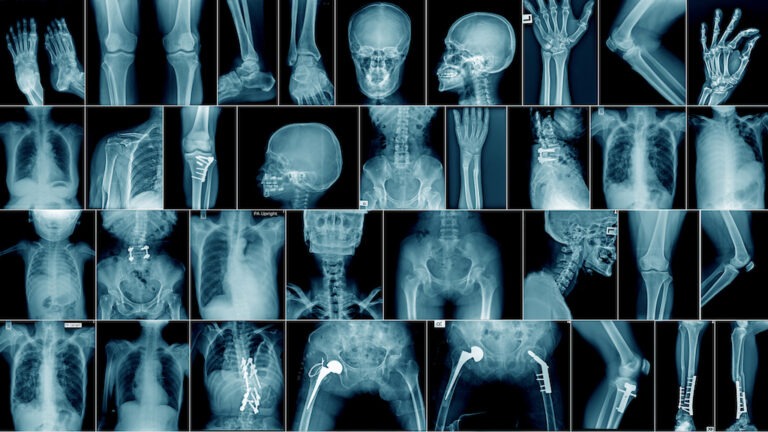
Company Builds AI Text Generator Too Dangerous for Public Release

As the age of automation draws increasingly nearer, the gatekeepers of this exciting, yet frightening, technology are being forced to make ethical decisions on whether or not their A.I. will better humanity or cause its downfall. And just recently the creators of the machine learning research group OpenAI, backed by Elon Musk, Sam Altman, and Reid Hoffman, decided one of their creations was too dangerous to release in full as they realized their AI was too good at generating “deepfakes for text.”
The nonprofit research firm’s GPT2 text generator was fed over 10 million news articles from Reddit – about 40 GBs worth of text – to generate an intuitive program that completes any input sentence into a full-length news article — a fake news article.
A demonstration of the technology can be seen in the below video posted by the Guardian, which shows what happened when the first sentence of an article was input to the bot. Within seconds, the tool generates a fabricated paragraph that reads in a journalistic tone, and sounds like it could actually be reporting legitimate news.
Entering the opening lines of Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice and George Orwell’s 1984, had the same effect – without hesitation, the bot filled in the next paragraphs with sentences that read fluently and made perfect sense, albeit they weren’t the sentences from the book.
In a world rife with fake news, ambiguity, and attempts to mislead through media, Musk and his colleagues must have immediately realized the implications GPT2 had when it came to exacerbating these issues.
Just imagine if someone could take an entire article and replace it with deepfakes generated by an AI algorithm such as this?
It would be even worse if only small snippets of an article were replaced by erroneous outputs from the bot, creating slight variations, imperceptible to those who wouldn’t know to verify what they were reading, while the rest of the document might look identical to the real thing.
But then there’s also the really fun applications for this technology that Musk and company certainly played around with for a while. Like the fake news article they had the bot create that outlined the unprecedented discovery of a unicorn the bot named Ovid’s Unicorn:

But while OpenAI had the prescience to withhold their research from the public, it seems this level of technology could easily be created by another research group with fewer ethical reservations.
The journalists at the Guardian also decided to feed the first two paragraphs of their article on GPT2 to itself, out of curiosity of what it might say. Though the results were entirely fake, it wasn’t necessarily the eerie sentience one might have expected from an intelligent bot. Though it said it hoped its creators would release a safe and useful version of it to the public.
Nice try GPT2, but we’re not falling for your devious tricks.
In addition to deciding their text-generating tool was too dangerous to be publicly released, Musk recently decided to leave OpenAI due to what he said was some of the decision making occurring there. It’s unclear whether this had anything to do with the conversations around GPT2.
But in all of the fear surrounding the repercussions this technology could have for news and media, there is certainly one group looking forward to the potential these bots portend: students looking for an easy way out of writing that English essay. Their poor teachers…
For more on the rise of artificial intelligence check out this episode of Deep Space :
Scientists Are Now Using Sound Waves to Regrow Bone Tissue
The future of regenerative medicine could be found within sound healing by regrowing bone cells with sound waves.
The use of sound as a healing modality has an ancient tradition all over the world. The ancient Greeks used sound to cure mental disorders; Australian Aborigines reportedly use the didgeridoo to heal; and Tibetan or Himalayan singing bowls were, and still are, used for spiritual healing ceremonies.
Recently, a study showed an hour-long sound bowl meditation reduced anger, fatigue, anxiety, and depression, which is great news for mental health. But now, a new study out of the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology in Australia, showed physical healing using sound waves.
Scientists used high-frequency soundwaves to turn stem cells into bone cells in a medical discipline called ’tissue engineering,’ where the goal is to rebuild tissue and bone by helping the body to heal itself.
The researchers shot sound waves at tissue cells for 10 minutes a day over the course of five days. This magnified image shows stem cells turning into bone cells after being treated with high-frequency sound waves.