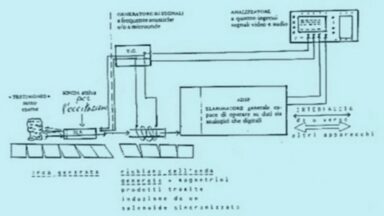
A Glowing Rogue Planet Was Spotted Drifting Near Our Solar System
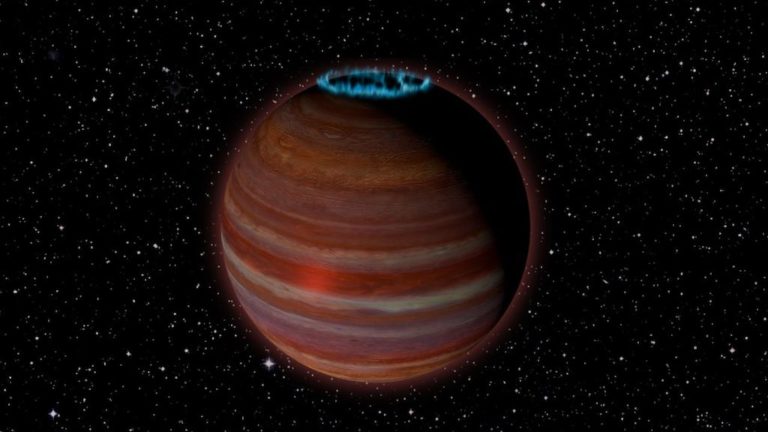

In 2016, scientists stumbled upon a massive object just beyond our solar system, which they believed was a ‘failed’ brown dwarf star. Now, a paper published in the Astrophysical Journal has reclassified it as a rogue planet and it’s got some pretty bizarre characteristics.
Given the rather boring, scientific moniker SIMP J01365663+0933473, this newly classified planet is just below the threshold of brown-dwarfdom, typically set at 13 times the size of Jupiter. Weighing in at a mere 12.7 times the size of Jupiter, this mega-planet also has a magnetic field 200 times stronger than the gas giant we know. And it’s floating through space, untethered to any star.
Scientists observed some bright and powerful auroras near the planet’s polar regions due to its intense magnetic field – think the Northern Lights like you’ve never seen them before. This happens when charged solar particles bombard the planet, before being ionized by its magnetosphere.
The planet is relatively young, about 200 million years-old, and is drifting about 20 light-years away from us – a relatively short distance on a cosmic scale.
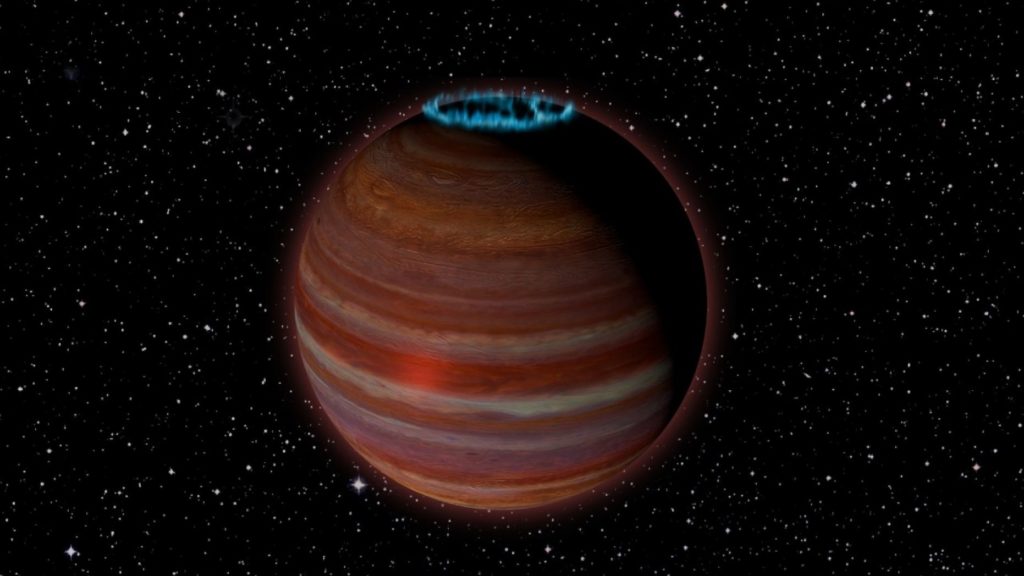

Artist’s representation of SIMP Credit:Credit: Caltech/Chuck Carter; NRAO/AUI/NSF
Sometimes rogue planets can become “captured” by another star and join the ranks of its solar system. This planet is currently being pulled by the gravitational force at our galactic center, but if it came close enough to our sun it could be sucked into its gravitational pull. In this scenario, a rogue planet might find itself crashing into other planets in our neighborhood, knocking into them like a pool cue and causing mass chaos.
This is unlikely to happen with SIMP, but scientists believe there could be a multitude of these rogue planets floating through the galaxy and occasionally wreaking havoc on unsuspecting solar systems, ahem, Nibiru?
The discovery of SIMP came about through the detection of its strong auroral radio emissions and scientists hope to use this method to discover more rogue planets. It would have been nearly impossible to have detected it otherwise, due to its lack of a parent star.
As we find more of these rogue planets in our cosmic region, it will hopefully tell us more about our place in the galaxy and what our future trajectory looks like. This prospect is exciting as long as we don’t find ourselves on a terminal collision course.
Have Recent Solar Flares Opened Energy Portals?

On October 28, 2021, a massive solar flare unleashed a blast of charged particles in Earth’s direction.
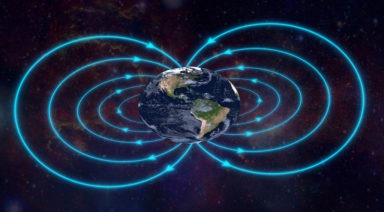
This geomagnetic storm resulted in a display of stunning auroras thanks to our planet’s protective magnetosphere. But did this powerful solar event also open temporary energetic portals?
On Oct. 28, a Category 3 geomagnetic storm erupted from the Sun’s surface reaching earth a few days later. This classification comes from the national oceanic and atmospheric administration’s space weather scale.
A level 3 geomagnetic storm is considered strong and can result in minor disturbances to high-frequency radio signals and low-frequency radio navigation. It also leads to auroras visible at much lower latitudes than usual, including as far south as Oregon and even Illinois.
Matias De Stefano, host of the Gaia series Initiation, happened to be in Oregon during this profound solar event.
These storms from the magnetic field of the Sun affect all the planets around, and of course when they hit Earth, they change the pattern of the magnetic field of the planet,” De Stefano said. “So, that opens portals all the time because it moves the energy of the planet and makes the geometrical patterns have to restore and readapt to something new.”
In 2012, NASA published a paper titled, “Hidden Portals in Earth’s Magnetic Field,” in which it explained that a scientist had discovered what the space agency refers to as x-points, or portals where the magnetic field of the Earth connects to the Sun.
According to Jack Scudder, the lead physicist who discovered these portals, this phenomenon creates an uninterrupted connection to the Sun‘s atmosphere 93 million miles away. But what effect does this have for us here on Earth?