Passive Stretch to Open the Hips
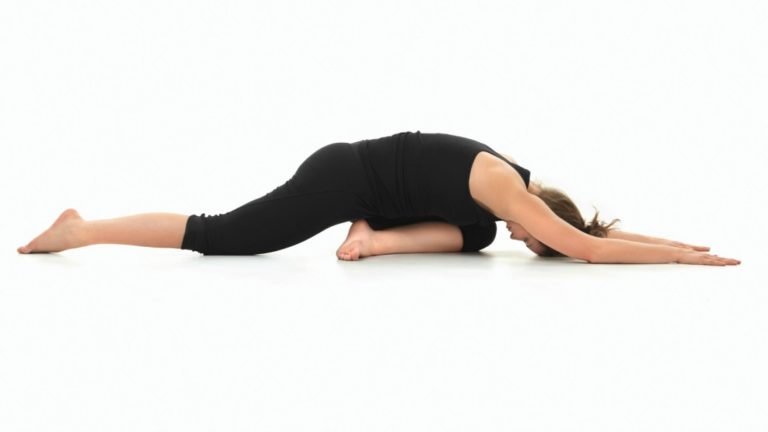

Open hips are a kind of holy grail in the world of yoga. If your hips are tight some of the most basic movement in yoga will be an eternal challenge. Lotus and half lotus posture is almost taken for granted in traditional yoga practices. Not every student of yoga has naturally open hips.
Those that are born tight suffer and strive to open their hips. If you rush the process of opening the hips the weaker joints nearby, most often the knees, take the brunt of the pressure and can often end of up injured.
While it’s easy to push hard and over-exert yourself in any activity it’s harder to find the perfect balance between activation and release that will create health and healing in the body. If you have tight hips and you want them to open your mission is not to open your hips but to find that healing balance.
If you practice a traditionally active style of yoga like Ashtanga Yoga and your hips are tight then it can be very useful to supplement your daily practice with some additional passive stretching. There are many stretches that can help target your hips, but this one will prepare your body especially well for lotus and half lotus position.
Called double pigeon, you want to go into this movement with a relaxed, almost meditative mind. Do not seek to strive or force anything. Bend both knees about half way and stack the right leg on top of the left so that the right foot is on top of the left knee and the left foot is underneath the right knee. If it’s uncomfortable to sit here then just stay in position.
If you are comfortable fold forward and relax all unnecessary effort. Breath freely and effortlessly. Surrender your body into the floor and place your mind on the inner body. See if you can feel the external rotation of your hip joints. Place your mind deep within the pelvis and be sure not to fight or struggle with yourself. Just be exactly where you are. Hold the first side for between one and give minutes. Then switch sides.
Adding a passive stretch like this to your daily yoga practice can help relax the mind and body and balance what may be a sometimes overly aggressive attempt to force the body to open. If you do try this posture the calm, meditative mind is perhaps the most beneficial aspect of the movement.
Standing Tall: Why Posture Matters

Remember how your mom used to always lecture you to stand up straight? Well, she might have made some mistakes over the years (that outfit in your 5th grade school picture), but on this one, she’s right. Posture matters more than you may think.
First, let’s talk about your body, starting at the top. Each inch your head is forward of your shoulders doubles the amount of weight it puts on the rest of your body. Although the average head only weighs between 8-10 pounds, your upper back (and then lower back and hips) will become misaligned if your head “lives” in a forward position – all in an attempt to balance your now-too-heavy head.
And, unless you sit in an ergonomically perfect workstation, chances are you round forward over your keyboard or laptop like something straight out of the latest episode of the “Walking Dead.” Most of us, sadly, are in the process of developing this posture. Blame the Internet (we’re talking to you, Mark Zuckerberg) or your boss (for making you work too much).
What happens to our bodies? Back pain, neck pain, hip pain and knee pain. And, let’s not forget your breathing. Collapsing forward compresses your lungs, reducing their capacity by 30 percent or more. Your organs can’t function properly, and neither can your muscles, joints, or connective tissue.
Posture also matters for your mental health. Good posture allows you to breathe more fully, calming your nervous system, which can help with everything from good sleep to good moods. Plus, standing up tall makes you feel more confident. Slouching pulls your energy downward, even making walking and balance more difficult.
What to do? First, analyze your own posture. Do your shoulders slouch? Is your head forward? Do you have back or neck pain? When you walk do you have a tendency to lean forward and feel like you’re lifting your knees towards you?
Since it is vital to have extension in the upper torso in standing posture, the starting place is simply awareness of how you’re standing or sitting. Imagine lifting out of your pelvis, shoulders back, head looking slightly above the horizon.
Don’t spend too much time sitting at your desk, especially in bad posture. Take a walk. Inhale your arms overhead and slightly back. Regularly engage your lower trapezius to draw your shoulders away from your ears, and your rhomboids to draw your shoulders together.
And balance the forward posture with a lot of back bends. Stretch your pecs and anterior shoulder muscles with anahatasana pose (think child’s pose with your hips over your heels, reaching your tailbone and chest away from each other). Camel pose has been called the “antidote to sitting” because it stretches the entire front of your body.
If you have access to a Pilates reformer, you’re in luck. Do seated arm circles to take your shoulders through a weighted stretch, and turn around for chest expansion to, well, expand your chest and your lung capacity. Or just lie down on a mat, extending arms and legs long on the floor, and lift up, fluttering arms and legs in opposition while breathing deeply.
Most importantly, throughout your day, remember to stand up straight. Don’t slouch. Just listen to mom on this one. You can still argue about your clothes, your politics, and what’s for dinner. On posture, she’s right.