Could Discovery of 9.7 Million Year Old Teeth Rewrite History?
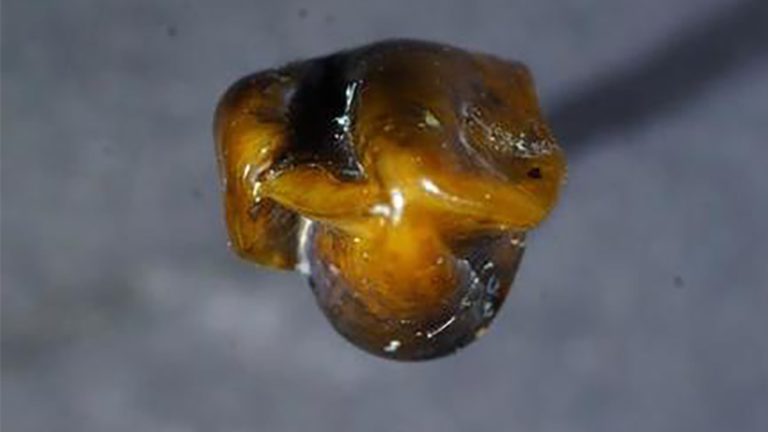

A recent archaeological find in Germany has the potential to change our understanding of human history. Researchers recently discovered a pair of teeth in a sedimentary layer dating back almost 10 million years. Now, after waiting an entire year to publish their discovery, the team says they believe their find came from a hominid species, potentially shifting the official timeline of our ancient ancestors. Could this discovery of fossilized teeth rewrite human history?
Archeological Find of the Century
It’s been 80 years since a fossil of this nature was discovered and nearly 40 years since the discovery of ‘Lucy,’ the Australopithecus afarensis, our hominid ancestor who eventually evolved into the genus: homo. Lucy died around 3.18 million years ago in what is now Ethiopia. She has since been the basis for our understanding of the origin of our ancestors and their subsequent migratory paths throughout the world. Lucy has led us to assume that humans originated in Africa and left no earlier than 120,000 years ago.
Now, under the guidance of paleontologist and geologist Herbert Lutz, a team has found an upper right molar and upper left canine, that they believe resembles either the hominid species, Ardipithecus ramidus or Australopithecus, like Lucy. If this hypothesis holds up, it would suggest two things; that our hominid ancestors were present outside of Africa and that they, or a close relative, existed millions of years earlier than previously thought.
But some say that Lutz’s discovery isn’t as profound as he believes and that the canine tooth likely belonged to a ruminant animal, like a deer, cow or sheep. They also say that the molar is more likely to have originated in a non-hominoid species known as Pliopithecoids who were known to have lived between seven and 17 million years ago. This would not be a major discovery as we’re more closely related to baboons than we are to Pliopithecus.
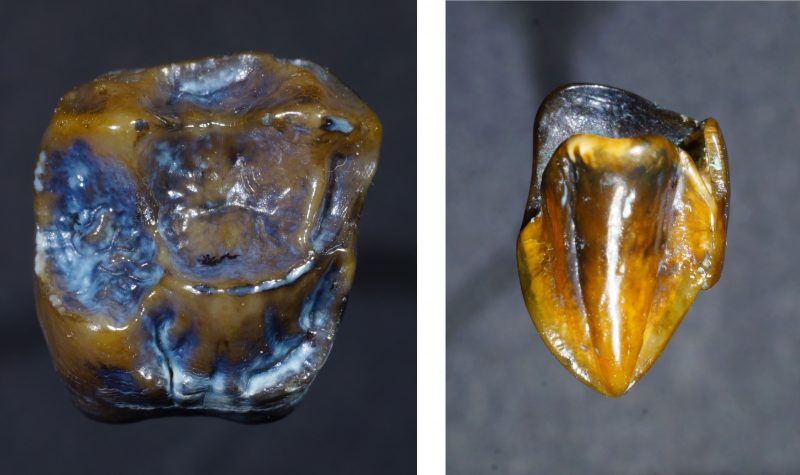

9.7 Mya molar and canine via inverse.com
Lutz is undeterred by his colleagues’ criticisms, saying that since the two teeth were found together after 20 years of painstaking excavation, and with no other similar discoveries in that area, they must have come from the same mouth. He also didn’t jump to conclusions, spending a year doing the necessary research before going public. He found evidence that the teeth had different characteristics from Pliopithecus and that they came from a sub-adult specimen that would have been heavier than the non-humanoid species.
New Archeological Discoveries
The teeth were recovered in an area near the Rhine River, fossilized within a layer of sedimentary rock, dating 9.7 million years old. The site where they were found, known as Eppelsheim, has only produced nine or ten finds within the past couple centuries, making this discovery rare and lending to the possibility that the two teeth came from the same jaw.
Lutz is under the assumption that this was a previously unknown great ape with hominin resemblances that was part of a line of species that fall somewhere within our evolutionary history. His discovery is one of several that have challenged the timeline held by mainstream archeology, that believes hominids evolved in Africa and didn’t cross into Europe until about 2 million years ago.
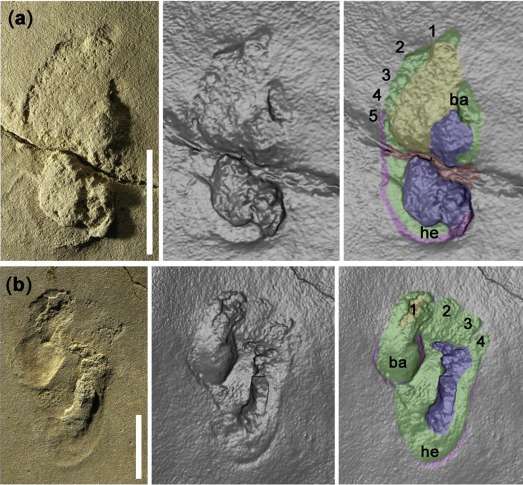
Other recent findings have suggested the possibility of hominid species in areas of Europe before what was previously thought possible. A discovery of fossilized footprints from a bipedal ancestor were found on the modern day island of Crete in Greece. These footprints date back 5.7 million years and were also discounted by mainstream archeologists as having a hominid provenance. Other sets of fossilized hominid teeth have been found outside of Africa, in places like Greece and Bulgaria and were dated over 7 million years old from the Miocene epoch.
Although the presiding opinion of mainstream archeology can be stubborn and tough to change, there seems to be new evidence everyday challenging that narrative. Could this discovery lead to new insight and a paradigm shift in our perception of history?
The History of Lemuria: Discover the Lost Continent
Lemuria, also referred to as Mu, was a vast, ancient continent said to have existed in the Pacific Ocean, inhabited by an advanced and spiritually developed civilization. It significantly influenced human evolution and left a legacy that endures to this day. In this article, we explore what Lemuria was, its origins, evolution, and impact on human history.
Table of Contents
- What Was Lemuria?
- Origins and Evolution of Lemuria
- Life in Lemuria
- Lemurian Technology and Knowledge
- The Relationship Between Lemuria and Atlantis
- The Fall of Lemuria
- The Legacy of Lemuria
What Was Lemuria?
Lemuria was a continent located in the Pacific Ocean, home to one of the earliest advanced civilizations on Earth. The Lemurians were highly spiritual beings who lived in perfect harmony with their surroundings. Their civilization was known for its profound knowledge of energy and its ability to manipulate it for the well-being and evolution of their society.
The Lemurian civilization thrived for thousands of years, developing advanced technologies that allowed them to build great cities and temples dedicated to meditation and spiritual connection. Lemuria was also a center of knowledge and wisdom, where various spiritual and scientific disciplines were taught and practiced. The Lemurians were known for their telepathic communication abilities and their capacity to access higher dimensions of existence, which enabled them to reach high levels of evolution and consciousness.
In Gaia’s series Initiation, experts examine the origins of many of the legends surrounding Lemuria throughout the Pacific Rim, as well as the clues that lead to Mu’s catastrophic demise.
Origins and Evolution of Lemuria
The history of Lemuria begins approximately 200,000 years ago when the Alithir, an advanced race, arrived on Earth to raise the planet’s vibration and encode the water. These highly evolved beings chose the continent of Lemuria as their home, establishing a civilization that would become a beacon of light and knowledge for the world.
The evolution of Lemuria was marked by a deep respect for nature and an advanced understanding of cosmic energies. The Lemurians developed technologies that allowed them to harness the energy of natural elements, using resonance and vibration to create sustainable structures and systems. Their ability to work in harmony with nature enabled them to thrive for thousands of years, maintaining a perfect balance between technological development and spirituality.
As Lemuria grew and evolved, it became a center of cultural and spiritual exchange. The Lemurians established relationships with other advanced civilizations of the time, sharing knowledge and technologies that would benefit humanity as a whole. This intercontinental cooperation allowed Lemuria to expand its influence and leave a lasting legacy in Earth’s history.
Life in Lemuria
Life in Lemuria was deeply integrated with nature and cosmic energies. The Lemurians lived in harmony with their surroundings, practicing an advanced spirituality that permeated every aspect of their existence. Their society was based on cooperation, peace, and balance, creating a rich culture of spiritual knowledge and practices.
- Peaceful society: The Lemurian society was characterized by its focus on peace and cooperation. There were no wars or conflicts, as everyone worked together for the common good.
- Natural homes: Lemurian homes were built with natural materials and energetically aligned with the environment. These sustainable structures provided comfort and harmony with nature.
- Spiritual education: From an early age, Lemurians received an education focused on spiritual development and connection with the universe. This allowed them to grow with a deep understanding of their place in the cosmos.
- Telepathic communication: The Lemurians had telepathic abilities, facilitating effective and profound communication among themselves. This eliminated misunderstandings and promoted greater social unity.
- Holistic health: Medicine in Lemuria was holistic, combining spiritual and scientific knowledge. They used energy and medicinal plants to heal and maintain well-being.
- Community rituals: Ceremonies and rituals were an essential part of Lemurian life, strengthening social cohesion and connection with cosmic energies. These events included collective meditations and celebrations of natural cycles.
- Relationship with nature: Daily life was synchronized with natural cycles, respecting and honoring the Earth and all its beings. This respectful relationship ensured the sustainability and abundance of resources.
Lemurian Technology and Knowledge
The Lemurian civilization was known for its advanced technology and profound understanding of natural energies. The Lemurians developed various technologies that allowed them to live in harmony with nature and harness cosmic energies for their benefit.
- Crystal energy: The Lemurians used crystals to store and channel energy. These crystals were essential in their healing and communication technologies.
- Resonance technology: They used resonance and vibration for construction and healing. This technology allowed them to create structures and regenerate tissues using specific frequencies.
- Solar energy utilization: Solar technology was highly advanced in Lemuria. They used devices to capture and store solar energy, providing a sustainable energy source.
- Coded water systems: The Lemurians encoded water with specific energies for healing and growth. This knowledge improved the health and vitality of their crops and themselves.
- Light ships: They developed ships capable of traveling through dimensions using light and cosmic energy. These ships facilitated contact with other advanced civilizations.
- Sacred geometry knowledge: Sacred geometry was used in all their constructions and technologies. Geometric patterns ensured energetic alignment and resource efficiency.
- Planetary energy networks: They created a network of connected energy points that facilitated energy transfer and long-distance communication. This network maintained balance and harmony throughout Lemuria.
The Relationship Between Lemuria and Atlantis
Lemuria and Atlantis were two advanced civilizations that existed during different periods, though there was a time when they coexisted and maintained contact. Both civilizations shared knowledge and technologies, establishing a relationship of cultural and spiritual exchange. The Lemurians and Atlanteans collaborated on several projects, mutually benefiting from each other’s discoveries and advancements.
The relationship between Lemuria and Atlantis was based on cooperation and mutual respect. The Atlanteans, who emerged after the Lemurians, adopted many of the spiritual and technological practices developed in Lemuria. This exchange allowed both civilizations to reach high levels of evolution and consciousness, significantly influencing the progress of humanity.
However, as both civilizations grew, differences in their approaches and philosophies began to emerge. While the Lemurians focused more on spirituality and harmony with nature, the Atlanteans began to develop technologies aimed at control. These differences eventually led to tensions and conflicts that contributed to the fall of both civilizations.
The Fall of Lemuria
The fall of Lemuria was a cataclysmic event that marked the end of a golden age of wisdom and peace. According to various esoteric traditions, Lemuria was destroyed by a series of natural disasters, including earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, that submerged much of the continent into the Pacific Ocean. This event was seen as a necessary energetic rebalancing of the Earth.
Before their fall, the Lemurians knew their time was coming to an end. Many of them migrated to other parts of the world, carrying with them their knowledge and traditions. These survivors established new communities in regions such as Asia, the Americas, and Africa, where they influenced the development of local civilizations and planted the seeds of new spiritual cultures.
Despite the physical destruction of Lemuria, its legacy continued through the stories and teachings passed down by the survivors. These stories became the foundation of many mythologies and belief systems around the world, keeping the memory of Lemuria alive and preserving its contribution to the spiritual evolution of humanity.
The Legacy of Lemuria
The legacy of Lemuria is evident in various spiritual and cultural traditions around the world. The knowledge and practices of the Lemurians were integrated into the cultures of Asia, the Americas, and Africa, influencing their belief systems, ceremonies, and social structures. This legacy can be seen in the similarities between the mythologies and spiritual practices of these regions.
The Lemurian teachings on connecting with nature and utilizing cosmic energies have endured through the centuries. These teachings are reflected in practices such as meditation, the use of crystals for healing, and the application of sacred geometry principles in architecture. The influence of Lemuria is especially notable in indigenous wisdom and shamanic traditions.
Today, many seekers and spiritual communities continue to explore and honor the legacy of Lemuria. Through study and spiritual practices, they strive to revive ancient knowledge and apply it to the modern world. This renewed interest in Lemuria highlights the ongoing relevance of its wisdom in the quest for balance and harmony with nature and the cosmos.