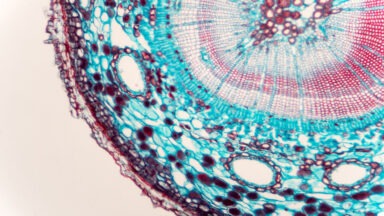
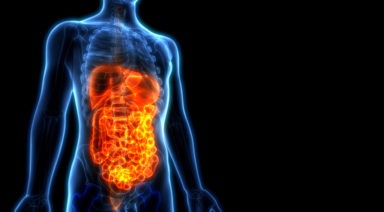
New Study Looks at Ancestor’s Gut Microbiome to Improve Health
A fascinating new study shows our gut microbiome has been experiencing a potentially catastrophic loss of diversity over the last millennium, possibly giving rise to various common chronic diseases. Is it too late to avoid irreversible damage to our health?
While most of us don’t ever think about it, we coexist with over 100 trillion microbes, the majority of which live in our gut and are essential to our health. Though the existence of the microbiome was first recognized in the 1990s, the full understanding of its importance and mechanisms is still in its infancy.
Dr. Alex Kostic is a microbiologist at Harvard Medical School, who has been studying the microbiome as a mediator of disease. “You know, this concept of the microbiome as a community of organisms living on humans and other mammals, and playing an integral role in our physiology really is a new concept, something that people have only been studying for the past 10-15 years or so,” Kostic said. “But what we’ve come to realize, as we study the ecology of all of the microorganisms living on humans, especially in the gut, is that it’s incredibly diverse, and pathogens are really the exception to the rule. Everything else has a lot of other roles that we’re still trying to tap into, but we can be fairly confident that they’re not driving disease in people.”
In their quest for a clear picture of the microbiome, researchers have recently turned to studying its history.
“What’s really gotten me interested in the history of the human microbiome, is this concept of being able to identify, if it exists, a ‘universal ancestral human microbiome,’ something that was common to all of us before the process of industrialization,” Kostic said.
Watch more:
Simple Tapping Technique Found to Lower Stress, Boost Immunity

In the latest research on emerging energy healing techniques, one modality is quickly proving itself to be unusually effective in bringing about immediate psychological relief and is done with just the tap of a finger.
Emotional Freedom Techniques — or EFT — are a powerful self-healing practice that seeks to address psychological issues by working with energy channels in the body. Also known as tapping, it combines modern psychological therapies with ancient healing technology.
Specifically, EFT incorporates the principles of acupressure, which involves the application of pressure to specific points in the body — thought for thousands of years to clear blockages along energy channels or meridians.
Dr. Dawson Church is a health and science writer who has been researching, practicing, and teaching EFT for decades.
“EFT’s history goes back thousands of years. Researchers have discovered mummies from Europe that are over 5,000 years old with these tapping points tattooed on their bodies. And acupressure is simply pressure on acupuncture points like we would normally use needling on them. Instead, we use pressure or fingertip tapping on those points.,” Dr. Church said.
“What we do with EFT is we simply organize several of the most potent points of acupuncture into a little ritual so you can remember to tap. The research shows that if you take somebody who’s stressed, the emotional brain — the central part of the brain, the limbic system — is highly active. When you have them tap while remembering a painful incident, it simply calms the brain down in a few seconds.”