Quadratus Lumborum and Mindful Back Health in Yoga

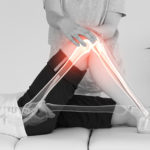
Low back pain is an increasing issue in our society dominated by poor posture, sedentary lifestyles, and chronic sitting patterns. The source of low back pain can vary, but a great deal of these muscular dysfunctions emanate from the quadratus lumborum muscles.
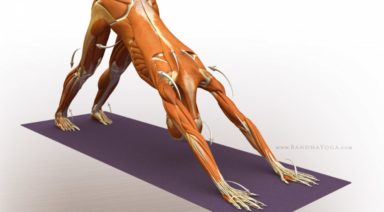
Most of us are quite familiar with the erector spinae muscles that travel from the hip crest/sacrum to various points up the vertebrae and ribs. These muscles function primarily as extensors of the back. Few people (including yoga teachers) are aware of the all-important quadratus lumborum muscles that are located deep toward the erector spinae.
The quadratus lumborum muscles sit on either side of the vertebrae. They originate on the iliac crest (hip bone) and insert on the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae and the 12th (last) rib.
When both sides contract, they extend the spine (and/or depress the ribcage from behind). When only one side contracts, the spine flexes laterally and/or elevates the ilium (hip) on that same side. In forced expiration, the quadratus lumborum will fix the 12 ribs.
When Back Pain Can Occur
Dysfunction and low back pain can settle into the quadratus lumborum under a few conditions:
- If the erector spinae are weak or inhibited (as they often are in chronic seated postures), the quadratus lumborum attempts to take up the slack and loading in back extension and spinal stabilization leading to overall muscle fatigue.
- If muscle imbalances build up across the pelvis (e.g., tight hip flexors), the lower vertebrae can shift into chronic excessive curvature (lordosis), which will shorten and weaken the quadratus lumborum and erector spinae.
- If poor posture and upper body muscle tension forms across the chest and shoulders, rounded-back posture (kyphosis) will pull the rib cage up and away from the hip crest. This places stress and drag on the quadratus lumborum and portions of the erector spinae.
- The deep gluteals (gluteus medius and gluteus minimus) are responsible for hip abduction and pelvic stabilization in walking and other gait patterns. If these deep gluteal muscles are weak and inhibited, the quadratus lumborum and tensor fascia latae have to compensate to stabilize the pelvis.
- Some physical experts have also found that tight hip adductor muscles (groin) can inhibit (through reciprocal inhibition) the gluteus medius muscles. As mentioned above, the quadratus lumborum muscle may compensate for the gluteus medius muscle’s lack of activity and pelvic stabilization.
How to Keep Your Back Healthy with Yoga
Understanding that the dysfunction residing in the quadratus lumborum is often the result of dysfunction and tension imbalances coming from other muscles, here are some initial approaches to maintaining health of the quadratus lumborum:
- Develop a strategy to maintain fluid balance in upper and lower body posture patterns to avoid chronic hip flexor tightness, back extensor tension, and loss of natural vertebral curvature and pelvic placement
- Stretch the chest, front of the shoulders, hip flexors, groin, and lower back frequently
- Strengthen back extensors and overall core stabilizers
- Strengthen and stretch deep gluteals to unload unnecessary engagement of the quadratus lumborum
- Engage in proper therapeutic treatments when discomfort and pain develop
Need help with yoga for back pain? Sign up for our Yoga Foundations Guide with Rodney Yee & Colleen Saidman Yee!
Do These Yoga Poses for Back Pain
Here are some basic, accessible stretches readily prescribed to restore and maintain flexibility in the quadratus lumborum muscles:
Child’s Pose
When aiming to stretch the quadratus lumborum muscles and other lower back musculature, I would personally recommend avoid using forward bends like Uttanasana (Standing Forward Bend), Paschimottasana (Seated Two Leg Forward Bend) and other similar poses.
Due to the nature of intervertebral disc compression in spinal flexion, these types of forward bends would be better served to actually involve engagement of the back extensors and transverse abdomen in order to extend the spine, shift the ‘flexion’ into the hips, unload the lower vertebrae and protect against disc compression.
Yoga Breathwork for Quick Sinus Relief

4 Minute Pranayama Kapalbhati Breathing Tutorial
Though it may seem counter-intuitive, breathing is another practice that can alleviate sinus discomfort. Try the following practices with a calm and relaxed demeanor, focusing on keeping your prana moving smoothly. You may wish to blow your nose, or better yet, use your neti pot before you try these exercises.
Belly Breathing
Lie on your back with your knees bent and your hands on your belly. Breathe deeply into the belly, focusing on expanding the belly like a buddha, then draw the breath and energy up through your ribs, chest and shoulders. Exhale the same way, deflating your belly, chest and shoulders, and squeezing all the air out of your belly. Find your own rhythm.
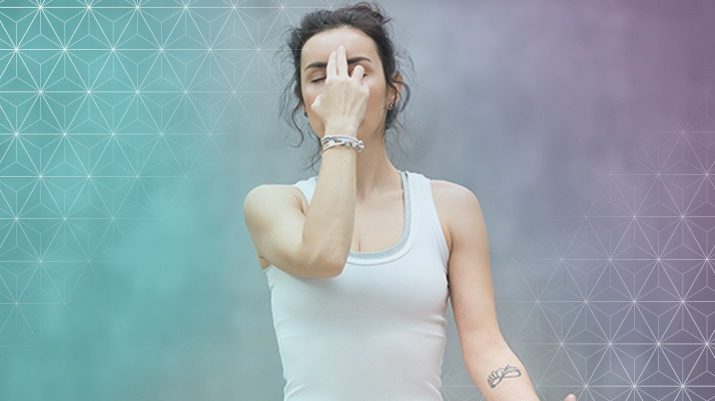
Calming Breath
Sit comfortably. Bring your right hand out in front of you, palm facing you. Fold your index and middle fingers into the palm. Place your ring finger on your left nostril to close it off. Breathe into the right nostril for two counts. Close off the right nostril with the thumb and hold the breath for two counts. Release the left nostril, exhale for two counts. Close off the left nostril and hold the breath for two counts. Try visualizing a square. If it feels uncomfortable to hold the breath, simply pause instead. Increase the count as you become comfortable, making sure that you are doing equal counts for each action.
Breath of Fire
In this practice, hold your hand over your navel, and practice forcefully exhaling out the nose repeatedly. Your belly should be pumping in and out. The force of the exhale will naturally draw in a new breath, so there is no need to inhale consciously. You may start this practice by gently panting, but it is important to eventually speed up the pace of this breath in order to stoke the “fire” of the breath.